Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world. It requires patients to take extra care of their health, including managing their blood sugar levels. While a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential, for many individuals with diabetes, prescription medications are also necessary. In this guide, we will delve into some commonly prescribed medications for diabetes and their uses.
Oral Medications
Oral medications are often the first line of defense when it comes to managing diabetes. These medications are taken by mouth and help control blood sugar levels by improving insulin utilization or reducing glucose production in the liver. Some commonly prescribed oral medications include:
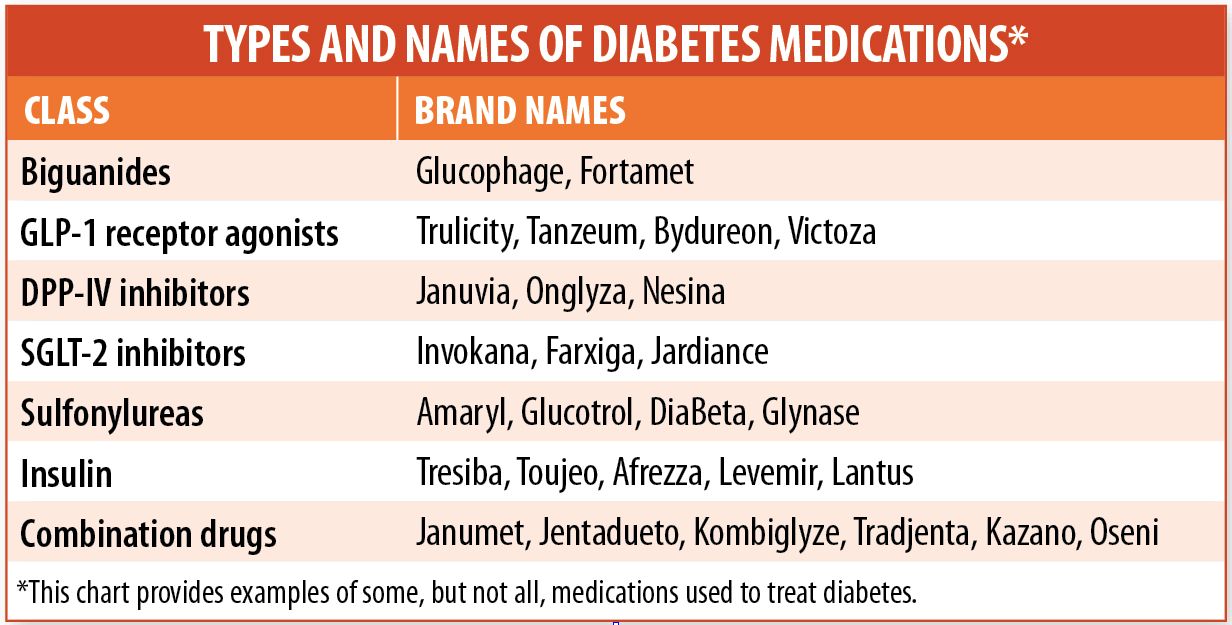
1. Metformin
Metformin is usually the first medication prescribed for people with type 2 diabetes. It works by reducing glucose production in the liver and improving insulin sensitivity in the body. Metformin is typically taken one to three times a day with meals. It is generally well-tolerated and has a good safety profile.
2. Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. They help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin release. Examples of sulfonylureas include glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride. These medications are usually taken once or twice a day before meals.
3. DPP-4 Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors work by blocking the action of an enzyme responsible for the breakdown of incretin hormones. These hormones help increase insulin release and decrease glucagon secretion. Examples of DPP-4 inhibitors include sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin. They are usually taken once daily and can be combined with other diabetes medications.
Injectable Medications
Sometimes, oral medications may not be sufficient in controlling blood sugar levels, or individuals may have difficulty tolerating them. In such cases, doctors may prescribe injectable medications to manage diabetes. Injectable medications include insulin and other non-insulin injectables.
1. Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are several types of insulin available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin. The type and dosage of insulin prescribed depend on the individual’s needs and blood sugar control goals. Insulin is injected using a syringe, pen, or insulin pump.
2. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists help regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin secretion, decreasing glucagon release, delaying gastric emptying, and promoting a feeling of fullness. Examples of GLP-1 receptor agonists include exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide. These medications are administered by injection once or twice daily, depending on the specific medication.
Conclusion
Prescription medications play a vital role in the management of diabetes. It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most suitable medications for their condition. Remember, medication alone is not enough, and a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and frequent blood sugar monitoring is key to effectively managing diabetes.