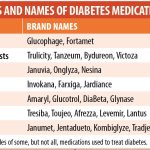
Prescription medications are an integral part of modern medicine, providing relief and treatment for a wide range of medical conditions. However, for some individuals, these medications can cause allergic reactions that range from mild to life-threatening. Identifying and managing prescription medication allergies are crucial to ensure the well-being and safety of patients. This article explores the identification and management of prescription medication allergies, including common symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment.
Understanding Prescription Medication Allergies
An allergy is an abnormal response of the immune system to usually harmless substances, such as medications. When exposed to a medication allergen, the immune system mistakenly recognizes it as a threat and triggers an allergic reaction.
Prescription medication allergies can present in various ways, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
Skin rashes or hives
Itching or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
Shortness of breath or wheezing
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Severe reactions such as anaphylaxis (life-threatening)
Diagnosing Prescription Medication Allergies
If a patient experiences symptoms that suggest a prescription medication allergy, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of the symptoms.
Diagnosing a prescription medication allergy typically involves:
Medical history: The healthcare professional will ask about any previous allergic reactions to medications and gather information about symptoms and their severity.
Physical examination: The healthcare professional will examine the patient for any visible signs of an allergic reaction, such as skin rashes or swelling.
Allergy testing: Depending on the severity and nature of the allergy, the healthcare professional may recommend allergy tests. These tests can include skin prick tests, blood tests, or patch tests to identify specific medication allergens.
Prevention and Management
Preventing prescription medication allergies is essential for patient safety. Here are some strategies to consider:
Medical history review: Before prescribing any medication, healthcare professionals should review the patient’s medical history to identify any previous allergies or adverse reactions.
Medication alternatives: In cases where a patient has a known allergy to a particular medication, healthcare professionals should explore alternative treatment options to minimize the risk of an allergic reaction.
Communication with healthcare providers: Patients should inform all healthcare providers, including doctors, nurses, and pharmacists, about their medication allergies to ensure proper consideration and avoid potential cross-reactivity.
Medication labeling: Pharmacists should clearly label medications with allergy warnings, allowing patients to double-check and verify the prescribed medication.
Emergency preparedness: Patients with known medication allergies should carry an epinephrine auto-injector and have an emergency action plan in place in case of an allergic reaction.
Treatment Options
Managing prescription medication allergies involves several treatment options, which vary depending on the severity of the allergic reaction. Some common treatments include:
Discontinuation of the medication: The first step in managing a prescription medication allergy is to stop taking the allergenic medication immediately.
Antihistamines: For mild allergic reactions, over-the-counter antihistamines can help relieve itching, hives, and other minor symptoms.
Topical treatments: In cases of localized skin reactions, healthcare providers may recommend creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and soothe the affected area.
Corticosteroids: For more severe allergic reactions, corticosteroids may be necessary to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response.
Epinephrine: In life-threatening reactions, such as anaphylaxis, prompt administration of epinephrine through an auto-injector can be life-saving.
Conclusion
Prescription medication allergies are an important consideration in modern healthcare. Identifying and managing these allergies are vital to ensure patient safety and well-being. By understanding the common symptoms, proper diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, and available treatment options, healthcare professionals and patients can work together to minimize the risks associated with prescription medication allergies and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.